What is Sustainable Procurement?
SPLC’s definition for Sustainable Procurement is purchasing that not only addresses internal business needs and goals such as cost and risk to the organization, but also provides external benefits – such as purchasing that strengthens the economy, society and the environment.
![]()
What do these external benefits include?
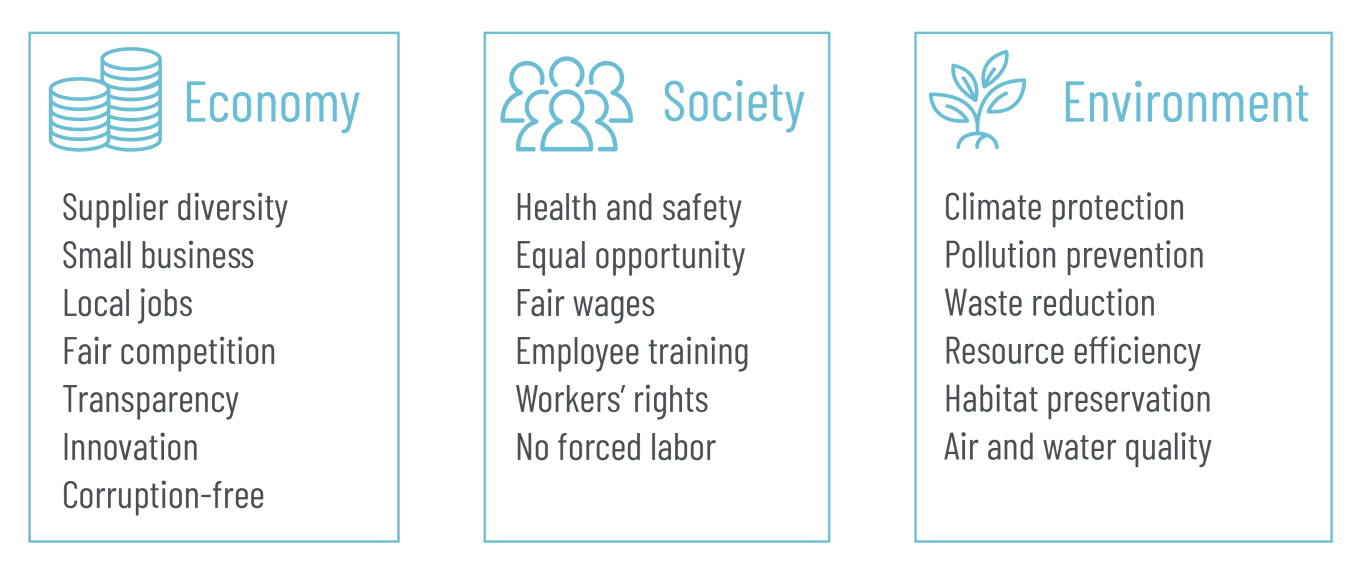
By strategically addressing internal goals like value for money and organizational strength while simultaneously generating critical external benefits for the economy, society, and the environment, organizations can enhance their brand reputation, mitigate risks, drive innovation, and ultimately secure long-term resilience and competitive advantage in an evolving marketplace.
The Importance of Sustainable Procurement
Our world faces urgent environmental, social, and economic challenges demanding bold action. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) provide a framework to build a sustainable future. Because many of these goals directly involve procurement, organizations must empower their purchasing departments to play a crucial role in achieving them.
An organization’s largest emissions footprint often lies within its supply chain. To truly maximize sustainable procurement, organizations must actively engage suppliers, as their supply chain is often the largest source of emissions. By setting clear expectations, providing support, and fostering open communication, organizations can empower suppliers to adopt sustainable processes. This collaboration reduces environmental impact, drives innovation, strengthens relationships, and builds a resilient supply ecosystem, ultimately leading to a more sustainable future.
Economic sustainability includes opportunities like promoting and supporting small businesses and local community development, while expecting all organizations to be transparent about their sustainability performance. Supplier diversity, for example, strengthens the economy by providing jobs and growth to minority-owned businesses and their communities. Organizations that integrate diverse-owned businesses into their procurement will not only build economic and professional vitality within these communities, but also:
-
Promote competition and widen the supplier pool
-
Drive down costs and improve product quality
-
Make supply chains more resilient and agile
-
Spur innovation and creativity
-
Strengthen brand recognition
Beyond economic benefits, supplier diversity promotes equal opportunity, fair wages, and professional development (social sustainability). It also bolsters environmental sustainability; diverse suppliers are often local, reducing travel distances for goods and services, and directly cutting Scope 3 supply chain emissions.
SPLC can empower organizations to overcome complex sustainability challenges by providing guidance and strategies for engaging suppliers, implementing robust labor policies, and fostering diverse and resilient supply chains. This holistic approach enables businesses to significantly reduce their environmental footprint, ensure human rights are upheld, and drive economic vitality across their entire value chain. Learn more about the benefits of SPLC membership.

